Model-Integrating Development (MID)
A promising way to develop flexible software systems is to use models as part of the system that are analyzed, modified and executed at runtime. The research group Database and Information Systems studies the development of such model-integrating systems.
Members: Marvin Grieger
Contact: Marvin Grieger
Cooperation: University of Koblenz-Landau
External Funding: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
Description:
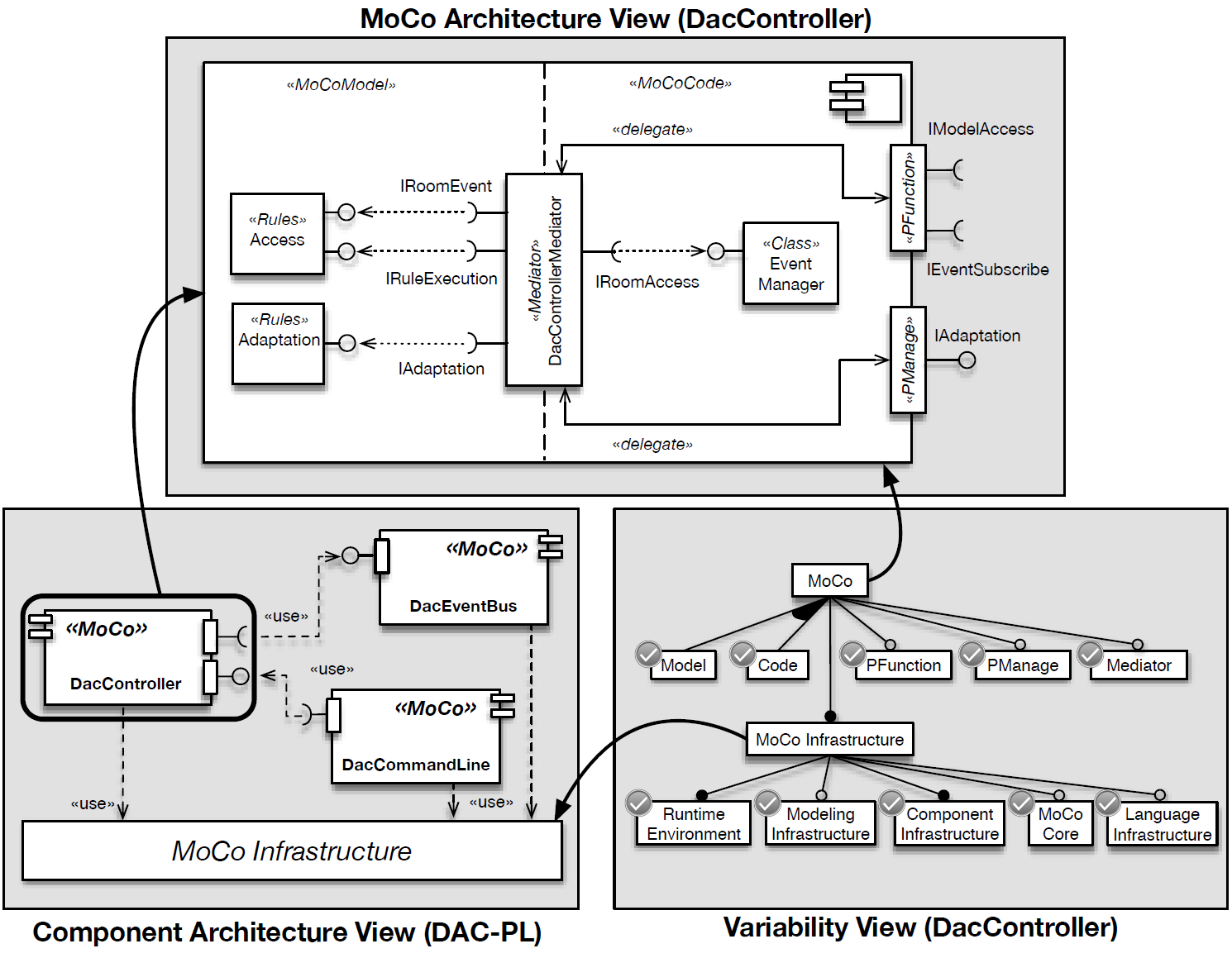
Software systems need to be modified continuously to suit new customer requirements. To support this endeavor, systems need to be flexible. They should be modifiable and changeable with reasonable effort and be able to adapt themselves permanently. A promising way to develop flexible software systems is to use models as part of the system that are analyzed, modified and executed at runtime.
Building such model-integrating systems is a challenging task. On the one hand, the design of Domain-Specific Modeling Languages (DSMLs) needs to be considered explicitly during the software development process. On the other hand, the systems need to be developed in a modular way by composing the system from building blocks.
Model-Driven (MDD) and Component-Based Development (CBD) are two established orthogonal approaches that can tackle the mentioned challenges. MDD is based on the use of models and modeling languages as first class entities to systematically engineer software systems. CBD enables the engineering of modular systems by facilitating a divide-and-conquer approach with reuse. However, combining and aligning the individual principles from both approaches is an open research problem.
The research group Database and Information Systems defines Model-Integrating Development (MID), an engineering approach that enables the systematic development of component-based, model-integrating software. MID combines principles from MDD and CBD and is based on the central assumption that models and code shall be treated equally as first-class entities of software throughout its lifecycle.